List of Roman Provinces
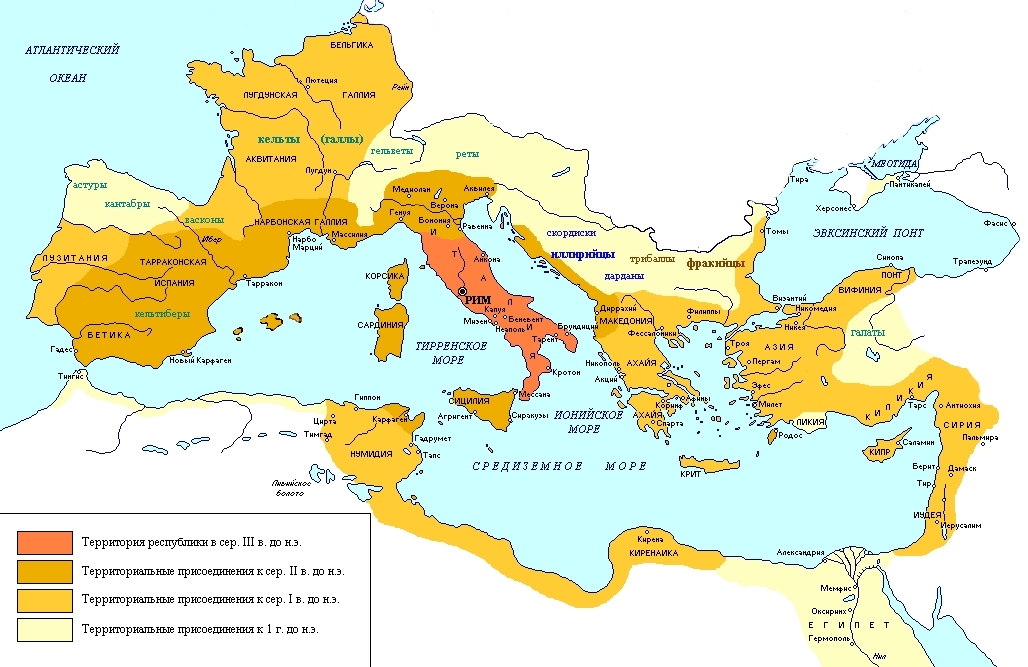 Map of the Roman Republic
Map of the Roman Republic
The Roman state was the largest empire of the Ancient world. During its peak in the 2nd century AD, it consisted of 36 provinces located across multiple continents. The Roman provinces are listed in the order of their establishment:
1. Sicilia (227 BCE)
2. Sardinia et Corsica (227 BCE)
3. Hispania Ulterior (197 BCE)
4. Hispania Citerior (197 BCE)
5. Macedonia (148 BCE)
6. Africa (146 BCE)
7. Asia (133 BCE)
8. Gallia Narbonensis (120 BCE)
9. Cilicia (92 BCE)
10. Crete et Cyrenaica (75 BCE)
11. Pontus et Bithynia (74-66 BCE)
12. Syria et Judaea (63 BCE)
13. Gallia Lugdunensis (52 BCE)
14. Belgica (52 BCE)
15. Aquitania (52 BCE)
16. Africa Nova or Numidia (46 BCE)
17. Aegyptus (30 BCE)
18. Illyricum (27 BCE)
19. Achaea (27 BCE)
20. Galatia (25 BCE)
21. Lusitania (19 BCE)
22. Raetia (15 BCE)
23. Noricum (15 BCE)
24. Moesia (15 BCE)
25. Pannonia (10 BCE)
26. Dalmatia (6 CE)
27. Germania Superior (16 CE)
28. Germania Inferior (16 CE)
29. Cappadocia (17 CE)
30. Mauretania Tingitana (40-41 CE)
31. Mauretania Caesariensis (40-41 CE)
32. Lycia et Pamphylia (43 CE)
33. Britannia (44 CE)
34. Thrace (46 CE)
35. Arabia (105 CE)
36. Dacia (107 CE)
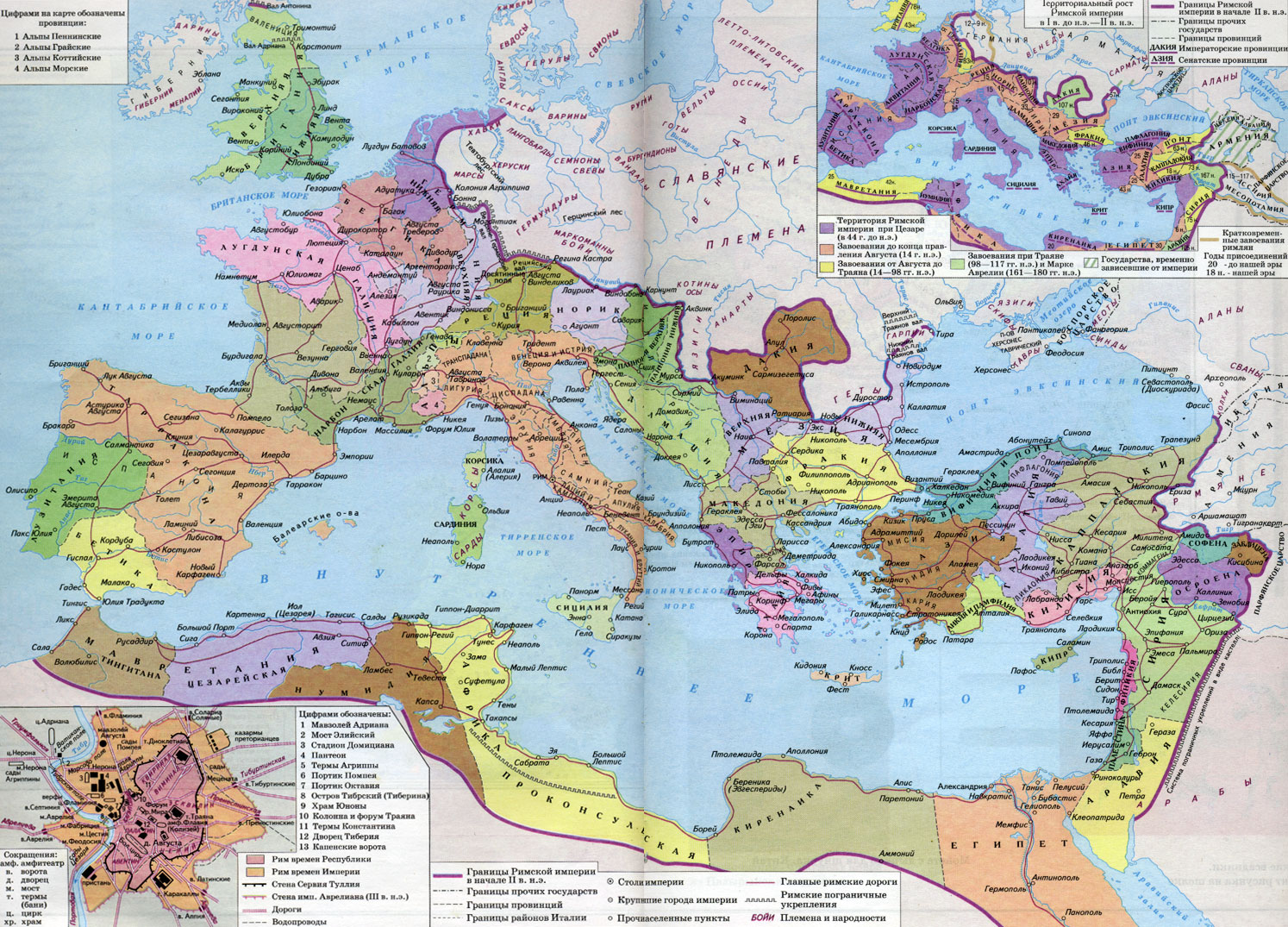 Map of the Roman Empire
Map of the Roman Empire
Related topics
Roman Republic, Roman Empire, Ancient Rome
Literature
Kuzishchina, V.I. (ed.). History of Ancient Rome. Moscow: Vysshaya Shkola, 2000. (In Russian) - 391 p.
Kovalev, S.I. History of Rome. Revised and expanded edition. Edited by Prof. E.D. Frolov. St. Petersburg: "Polygon" Publishing, 2002. (In Russian) - 864 p.


