Antiquity
Antiquity (from the Latin antiquitas meaning "ancient times") is a term used to describe a historical period associated with Greco-Roman civilization. This term was adopted in the early 18th century in the French language and originally referred to a specific type of art. The proliferation of studies in art history led to the narrowing of the concept to the confines of Greco-Roman antiquity. In pre-revolutionary Russia, the term "classical antiquity" was used.
Antiquity is generally divided into the following main periods:
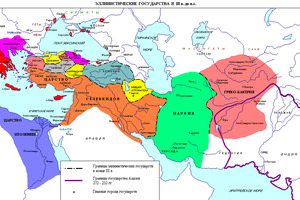
- Early Antiquity (8th century BCE – 4th century BCE): The flourishing of Greek city-states (polis) and the emergence of the Roman state.
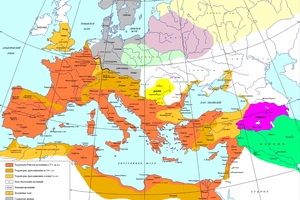
- Classical Antiquity (4th century BCE – 2nd century CE): The period of the widespread influence of Greek and Roman civilizations, from the era of Alexander the Great to the time of Marcus Aurelius.
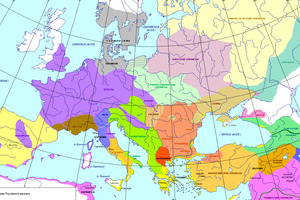
- Late Antiquity (3rd century CE – 6th century CE): The decline of the Roman Empire, from Commodus to the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE, the death of "the last Roman" Boethius (524 or 526 CE), and the closing of the Academy in Athens by Emperor Justinian in 529 CE.
The collapse of the Western Roman Empire marked the beginning of a new era known as the Middle Ages.
The chronological boundaries of antiquity can vary somewhat depending on the geopolitical context. For example, the peak of civilization in Ancient Greece occurred earlier than in the Roman Empire. Additionally, the civilization of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) emerged earlier and declined later than in the western part, where its structure was disrupted by the invading Germanic tribes. Nevertheless, the cultural heritage of antiquity (mostly in its late antique form) has been well preserved in the daily life, culture, language, and traditions of most modern Romance peoples and was subsequently passed on to other Mediterranean peoples (such as the southern Slavs, Arabs, Turks, Berbers, and Jews). It should also be noted that many elements of classical antiquity (traditions, laws, customs, etc.) were well preserved in the core regions of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire until the 11th century, prior to the arrival of the Seljuk Turks.
Key States and Peoples Influencing Antiquity in Europe:
Related topics
Ancient Greece, Rome, Celts, Germans, Ancient Egypt
Literature
- Soviet Historical Encyclopedia, edited by E.M. Zhukova. Moscow: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1973-1982.
- Dictionary of Antiquity, by Irshmer J., Jone R. Translated from German. Moscow: Progress, 1989. P. 37.