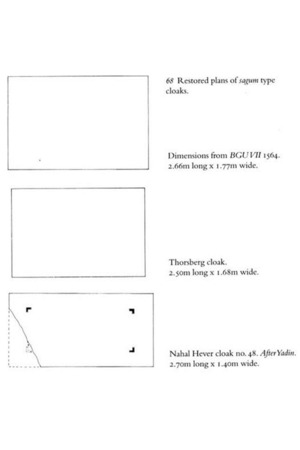
Sagum
The sagum (Latin: sagum) is a woolen cloak worn by Roman soldiers and officers. It was typically fastened on one shoulder with a fibula. Unlike the paenula, the sagum had a simpler design: it was a rectangle, not a semicircle, and did not have a hood. The cloak could be decorated with embroidery along the edges or corners, and sometimes the fabric was unraveled at the bottom into a small fringe.
Sagum was not very popular legionnaires and auxiliaries, but they used penula more often, as it is more practical. Sagum was more typical of officers, most often it depicted centurions. Traditionally, the cloak was fastened with a fibula under the neck or at the shoulder, it could also be attached to faleras or worn over the arm.
The sagum was not very popular amonglegionnaires and auxiliaries; they more often used the paenula, as it was more practical. The sagum was more typical for officers, most frequently depicted on centurions. Traditionally, the cloak was fastened with a fibula at the neck or shoulder and could also be attached to phalerae or worn draped over the arm.
Various archaeological finds and reliefs depict sagums, helping us better understand what they looked like and how they were worn:
- Stela of M. Aurelius Neon, a soldier in a sagum from legio II Traiana fortis. Brussels Museum, inv. №A. 2246. 222-235 AD.
- Relief from Adamclisi showing standard-bearers in sagums, early 2nd century AD.
- Stela with auxiliary soldier Aurelius Sabius, from legio II Traiana fortis. Alexandria, inv. № 252. 222-250 AD.
- Relief with a primipilus in a sagum, worn draped over the arm. Quintus Sertorius Festus - primipilus of the 11th Claudia Legion. Inv. № 28160. 1st century AD.
- Part of a relief with a centurion's sagum from the Museo Civico agli Eremitani, Padua, Italy. 25-0 BC.
The sagum was not very popular among legionaries and auxiliaries, who more often used the paenula due to its practicality. The sagum, however, was more typical for officers, most frequently depicted on centurions. Traditionally, the cloak was fastened with a fibula at the neck or shoulder and could also be attached to phalerae or worn draped over the arm.
Cloaks similar to the sagum were also found among other ancient peoples, particularly the Celts and ancient Greeks, and were primarily worn by military personnel:
- Macedonian tomb of St. Athanasios — an ancient Macedonian from the St. Athanasios tomb, the last quarter of the 4th century BC.
- Statue of a Gallic warrior with a sagum — found in Mondragon (Vaucluse, France). 1st century BC.
Reconstruction
The sagum is made from a rectangular piece of woolen fabric. The Romans wore cloaks in shades of red, brown, gray, and blue, with the imperial color being purple, though emperors more often wore the paludamentum. The typical color of an auxiliary cloak was green. Celts should choose shades of gray, blue, and green, while Greeks should choose red, gray, and terracotta.
For the reconstruction of the sagum, woolen fabric is used, the dimensions of which can vary depending on the height and build of the re-enactor.
Main steps in creating and wearing a sagum:
- Pattern — a rectangle of the desired size, approximately 1.5 by 2 meters.
- Decoration — optional, you can add embroidery along the edges or make a fringe.
- Securing with a fibula — for wearing the cloak on one shoulder or at the neck.
The sagum was an important part of the equipment of Roman soldiers and officers, and its reconstruction helps us better understand the material culture and military practice of Ancient Rome.
Sagum wearing options:
- Worn draped over the arm, reconstruction.
- Classic option with a fibula at the neck, reconstruction.
- Option fastened through phalerae, reconstruction.
Related topics
Paenula, Paludamentum, Legionnaire, Centurion, Phalerae, Toga, Chlamys, Himation, Fibula
Literature
William Ramsay, «Sagum», in William Smith, A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities, John Murray, London, 1875 pp. 1002.

 Gallery
Gallery